Headaches and migraines are two of the most common ailments that affect millions of people worldwide. They both cause pain and discomfort, but they are different in terms of intensity, duration, and accompanying symptoms. In this article, we will discuss the differences between migraines and headaches, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What is a headache?
A headache is a common condition that causes pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including tension, sinus congestion, dehydration, and stress. Headaches can range in severity from mild to severe, and can be classified as primary or secondary.
Primary headaches are not caused by an underlying medical condition, and include migraines, tension headaches, and cluster headaches. Migraines are typically severe, pulsating headaches that are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Tension headaches are usually mild to moderate in intensity and are often described as a tightening or pressure sensation in the head. Cluster headaches are rare but very severe, and often occur in cyclical patterns.
Secondary headaches are caused by an underlying medical condition, such as a head injury, sinus infection, or high blood pressure. These headaches are often more severe and require treatment of the underlying condition to alleviate the headache symptoms.
Treatment for headaches varies depending on the type and severity of the headache. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective for mild to moderate headaches. For more severe headaches, prescription medications or alternative therapies such as acupuncture or chiropractic care may be recommended.
If you are experiencing frequent or severe headaches, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to rule out any underlying medical conditions and to determine the best treatment plan for you.


Headaches are one of the most common health complaints, affecting millions of people worldwide. They can be caused by a wide range of factors, including stress, lack of sleep, dehydration, or certain foods or drinks. Some people are more prone to headaches due to genetic factors, hormonal changes, or other health conditions.
Symptoms of a headache can vary depending on the type and severity of the headache. Common symptoms include pain or pressure in the head, sensitivity to light or sound, nausea or vomiting, and difficulty concentrating. Some headaches may also cause visual disturbances or other neurological symptoms.
There are several different types of headaches, each with its own unique set of symptoms and causes. The most common types of headaches include:
Tension headaches: This is the most common type of headache, and is often described as a “band-like” pressure around the head. Tension headaches are typically caused by muscle tension or stress.
Migraines: Migraines are a type of headache that are often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. They are usually severe, and can last for several hours or days.
Cluster headaches: Cluster headaches are a rare but very severe type of headache that occur in cyclical patterns. They are often described as a stabbing pain around the eye or temple, and can last for several weeks or months.
Other types of headaches include sinus headaches, rebound headaches (caused by overuse of pain medication), hormonal headaches (related to menstrual cycles), and exertion headaches (caused by physical exertion).
Treatment for headaches depends on the type and severity of the headache, as well as any underlying medical conditions. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective for mild to moderate headaches. For more severe headaches, prescription medications or alternative therapies such as acupuncture or chiropractic care may be recommended. It’s important to speak with your healthcare provider if you experience frequent or severe headaches, as this could be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
Types of Headaches
Tension headaches: These are the most common type of headache, and are usually characterized by a dull, aching pain that feels like a tight band around the head. Tension headaches can be caused by stress, poor posture, and fatigue.
Migraines: As discussed earlier, migraines are a type of headache that are characterized by severe pain on one or both sides of the head, along with other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Cluster headaches: Cluster headaches are a type of headache that occur in cycles, and are characterized by severe pain on one side of the head, along with other symptoms such as red, watery eyes and a runny nose. Cluster headaches are more common in men than women.
Sinus headaches: These headaches are caused by inflammation of the sinuses, and are usually accompanied by symptoms such as facial pain, pressure, and congestion.
Rebound headaches: These headaches are caused by overuse of pain medications, and can occur when a person takes pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen too frequently or in large doses.
Hormone headaches: These headaches are often linked to hormonal changes, and are more common in women. They can occur during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause.
Exertion headaches: These headaches occur during or after physical exertion, such as exercise, aused by the expansion of blood vessels in the head.
There are several other less common types of headaches as well, such as thunderclap headaches, ice-pick headaches, and hypnic headaches. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you are experiencing frequent or severe headaches, as they may be a sign of an underlying medical condition.

Hangover headaches: These headaches occur due to excessive alcohol consumption, and are usually accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, and dehydration.
Allergy headaches: These headaches can be caused by various allergens such as pollen, dust, or certain foods, and are often accompanied by other allergy symptoms such as sneezing and congestion.
Caffeine headaches: These headaches can occur when a person consumes too much caffeine, or when they miss their usual caffeine intake. Symptoms can include throbbing pain, fatigue, and irritability.
Post-traumatic headaches: These headaches can occur after a head injury, such as a concussion, and can last for months or even years.
Hypertension headaches: These headaches occur due to high blood pressure, and are usually accompanied by other symptoms such as blurred vision and dizziness.
It’s important to note that some headaches can have overlapping symptoms, and that a thorough medical evaluation may be necessary to determine the exact type of headache and the underlying cause. Treatment options for headaches can vary depending on the type and severity of the headache, and may include lifestyle changes, medication, or other therapies.
the difference Migraine and Headache
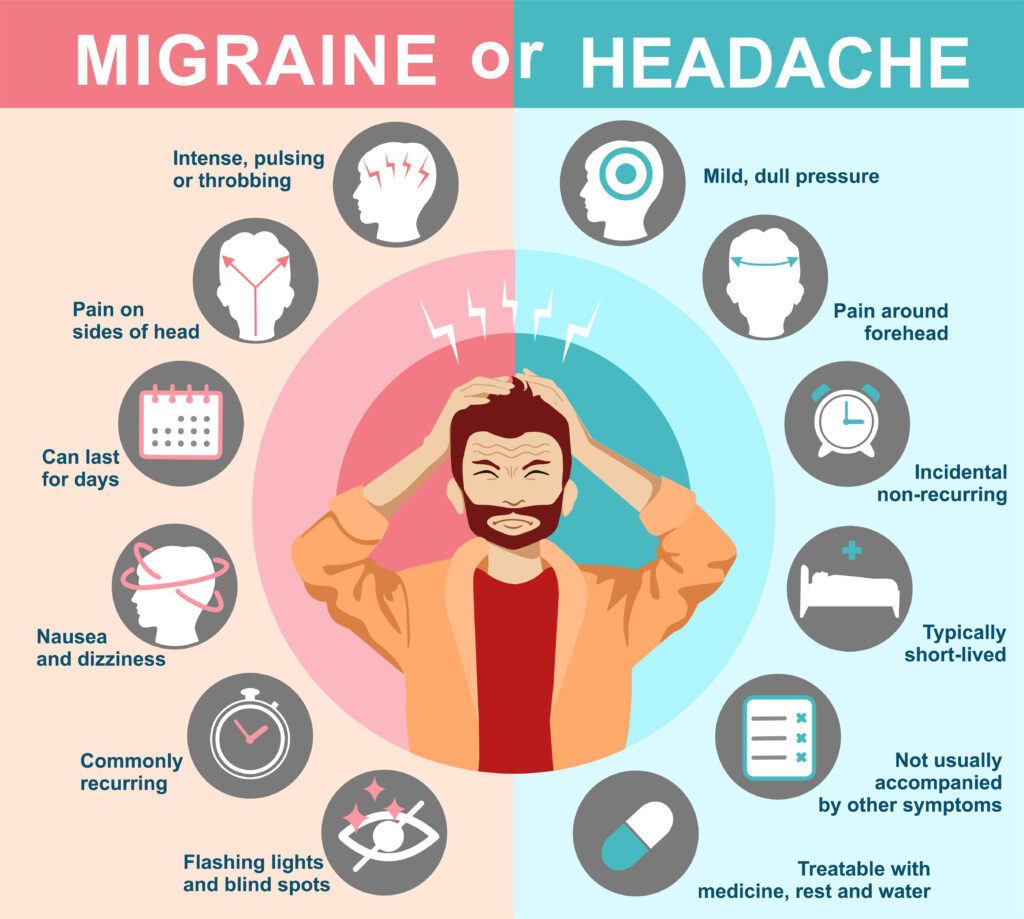
Migraine and headache are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same thing. A headache is a general term that describes any kind of pain or discomfort that is felt in the head, scalp, or neck region. On the other hand, a migraine is a specific type of headache that is characterized by a throbbing or pulsing pain on one side of the head, along with other symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and sometimes visual disturbances.
Headaches can be caused by a variety of factors, including tension, dehydration, sinus congestion, eyestrain, and more. They can range in severity from mild to severe and can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. In most cases, headaches are not a cause for concern and can be treated with over-the-counter pain relievers or other remedies.
Migraines, however, are a more complex condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental triggers, and hormonal changes. They are typically more severe than a regular headache and can last anywhere from several hours to several days. Along with the throbbing or pulsing pain on one side of the head, migraines can also cause nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances such as flashing lights or blind spots.

Another difference between migraines and headaches is the way they are treated. While over-the-counter pain relievers can be effective in treating headaches, migraines may require prescription medications specifically designed to treat this condition. Lifestyle changes such as stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and avoiding triggers such as certain foods or bright lights can also be helpful in managing migraines.
In summary, while a headache is a general term that describes any kind of pain or discomfort felt in the head, a migraine is a specific type of headache that is more severe and has additional symptoms such as nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Migraines can be caused by a variety of factors and may require specific treatment and lifestyle changes to manage effectively.
some more information about the differences between migraines and headaches:
Pain location: Migraine pain is typically felt on one side of the head, while headache pain can be felt on both sides.
Severity: Migraines are generally more severe than headaches, and can be debilitating for some people. Headaches are often less severe and can usually be managed with over-the-counter medications.
Duration: Migraines can last for several hours to several days, while headaches typically last for a few hours to a day.
Triggers: Migraines are often triggered by environmental factors such as stress, bright lights, and certain foods. Headaches can also be triggered by these factors, but are often caused by tension or sinus congestion.
Symptoms: Migraines often have additional symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Headaches may have additional symptoms such as a stuffy nose or pressure behind the eyes.
Family history: Migraines tend to run in families, so if you have a family member who suffers from migraines, you may be more likely to develop them too.
It’s important to note that not everyone experiences migraines or headaches in the same way, and there is some overlap between the two conditions. If you are experiencing severe or frequent headaches or migraines, it’s a good idea to speak with your healthcare provider to rule out any underlying conditions and to determine the best treatment plan for you.
types of common headaches
Headaches are a common ailment that most people experience at some point in their lives. There are several types of headaches, and the causes and symptoms of each type vary. Understanding the different types of headaches can help people identify what triggers their headaches and how to treat them. In this article, we will discuss the most common types of headaches and their causes.
Tension Headaches: Tension headaches are the most common type of headache, and they are often caused by stress, anxiety, and tension in the muscles of the neck and scalp. People describe tension headaches as a constant, dull pain that feels like a tight band around their head. These headaches are not usually severe, and they can be treated with over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Migraine Headaches: Migraines are a severe type of headache that can cause intense pain and other symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Migraine headaches are often characterized by a throbbing or pulsing pain on one side of the head. Migraines can be triggered by a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, certain foods or drinks, stress, and changes in sleep patterns. Treatment for migraines may include prescription medications, lifestyle changes, and avoiding triggers.

3. Cluster Headaches: Cluster headaches are a rare type of headache that occur in cycles or clusters. These headaches are often described as a sharp, burning pain that occurs on one side of the head, usually around the eye. Cluster headaches can be triggered by changes in sleep patterns, alcohol consumption, and cigarette smoking. Treatment for cluster headaches may include prescription medications, oxygen therapy, and nerve blocks.
4. Sinus Headaches: Sinus headaches occur when the sinuses become inflamed, usually due to an infection or allergy. These headaches are often described as a deep, constant pain in the forehead, cheeks, and bridge of the nose. Other symptoms of sinus headaches may include a runny nose, congestion, and fever. Treatment for sinus headaches may include antibiotics, decongestants, and pain relievers.
5. Rebound Headaches: Rebound headaches, also known as medication overuse headaches, occur when people overuse pain relievers for their headaches. These headaches can occur daily or almost daily and are often described as a dull ache that worsens with time. Treatment for rebound headaches involves stopping the overuse of pain relievers and gradually weaning off them.
there are various types of headaches, and identifying the type of headache can help determine the cause and the best course of treatment. It’s important to see a doctor if you experience severe or frequent headaches or if your headaches are interfering with your daily life.
Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are a type of headache that are characterized by severe, recurring pain on one side of the head. They are less common than migraines and tension headaches, and tend to affect men more than women.
Cluster headaches occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, with periods of frequent headaches followed by periods of remission. During a cluster period, headaches may occur several times a day, often at the same time each day, and can last between 15 minutes to three hours.
The pain associated with cluster headaches is typically described as a burning or piercing sensation that is focused around one eye or temple. Other symptoms may include redness and watering of the affected eye, nasal congestion or runny nose, and restlessness or agitation.
The exact cause of cluster headaches is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the trigeminal nerve, which supplies sensation to the face and can be activated by various triggers such as alcohol, tobacco, and certain medications.
Treatment for cluster headaches may include medication to alleviate pain and reduce the frequency of headaches, such as triptans or oxygen therapy. In some cases, nerve stimulation or surgery may be recommended for more severe or treatment-resistant cases.
If you are experiencing symptoms of cluster headaches, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Sinus headaches

Sinus headaches may be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergies, infections, and changes in air pressure. Inflammation or infection of the sinuses can lead to the buildup of pressure, which can cause pain and discomfort in the surrounding areas.
Symptoms of a sinus headache may include a deep, constant pain in the forehead, cheeks, or around the eyes, as well as pressure or fullness in these areas. Other symptoms may include a runny or stuffy nose, fever, and fatigue.
Treatment for sinus headaches may involve a combination of medication and self-care measures, such as over-the-counter pain relievers, decongestants, and saline nasal sprays. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat an underlying infection.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a sinus headache, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan. In some cases, more serious conditions such as migraines or tension headaches may be misdiagnosed as sinus headaches, so a proper evaluation is essential for effective management of symptoms.
In addition to the common types of headaches such as tension headaches, migraines, and sinus headaches, there are several other types of headaches that can cause discomfort and pain.
One type of headache is known as a rebound headache or medication-overuse headache. This occurs when an individual overuses medication for treating headaches, leading to a cycle of frequent headaches that may worsen with time. These headaches are typically treated by discontinuing the use of the offending medication and implementing a management plan with the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Another type of headache is called a thunderclap headache. This is a sudden, severe headache that can be indicative of a serious underlying condition, such as a ruptured blood vessel in the brain or a stroke. Individuals experiencing a thunderclap headache should seek immediate medical attention.
Hormonal headaches are another type of headache that are commonly experienced by women during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause. These headaches are thought to be related to changes in hormonal levels and can often be managed with lifestyle changes, medication, and hormone therapy.
Finally, exercise-induced headaches are a type of headache that are triggered by physical activity. These headaches may be caused by a variety of factors, including dehydration, poor posture, or changes in blood flow. Treatment for exercise-induced headaches may include rest, hydration, and modification of exercise routines.
It is important to note that headache symptoms can be indicative of a variety of underlying conditions, ranging from mild to serious. If you are experiencing frequent or severe headaches, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine an appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan.
What is migraine?
Migraines can last for several hours or even days, and can be very disabling for those who suffer from them. They can be triggered by a wide range of factors, including stress, hormonal changes, certain foods or drinks, and changes in the weather or altitude.
There are several different types of migraines, including:
Migraine with aura: This type of migraine is characterized by visual disturbances such as flashing lights or blind spots, which can occur before the headache begins.
Migraine without aura: This is the most common type of migraine, and does not have any visual disturbances or other sensory symptoms.
Chronic migraine: This is a type of migraine that occurs on 15 or more days per month, and can be very disabling for those who suffer from it.

Migraine Causes
The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Migraines are thought to be caused by changes in the brain and surrounding blood vessels. During a migraine, the blood vessels in the brain temporarily narrow, causing a decrease in blood flow and oxygen to the brain. This is followed by a widening of the blood vessels, which leads to a rapid increase in blood flow and causes the characteristic throbbing pain of a migraine.
Migraines can also be triggered by a variety of factors, including changes in hormone levels, stress, certain foods and drinks, sensory stimuli such as bright lights or loud noises, changes in sleep patterns, and physical exertion. For some individuals, migraines may also be triggered by specific environmental factors such as weather changes, high altitude, or exposure to certain chemicals.
In addition to these triggers, there are certain risk factors that may increase a person’s likelihood of experiencing migraines. These can include a family history of migraines, being female, being under the age of 40, and certain medical conditions such as depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders. Understanding the causes and triggers of migraines can be an important part of managing the condition and reducing the frequency and severity of migraines.
One of the most common triggers of migraines is stress. Emotional stress, as well as physical stress, can cause a migraine to develop. Other triggers include changes in sleep patterns, including both too much and too little sleep, changes in diet or eating patterns, and hormonal changes in women.
Migraines can also be triggered by environmental factors such as bright or flickering lights, loud noises, strong smells, and changes in weather or altitude. Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, blood pressure medications, and certain antibiotics, can also trigger migraines in some individuals.
In addition, some lifestyle factors may contribute to the development of migraines. These may include poor posture, lack of exercise, and poor eating habits. It is important to identify the specific triggers that cause migraines in each individual in order to develop an effective treatment plan.

Migraine triggers
Migraines can be triggered by a variety of factors, both external and internal. Identifying and avoiding triggers can help prevent or reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. Here are some common triggers:
Foods and drinks: Certain foods and drinks, such as aged cheese, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and foods containing the preservative monosodium glutamate (MSG), have been known to trigger migraines in some people.
Hormonal changes: Migraines can be triggered by changes in estrogen levels, which can occur during a woman’s menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause.
Environmental factors: Bright lights, loud noises, strong smells, and changes in weather or barometric pressure can trigger migraines in some people.
Stress: Emotional or physical stress can trigger migraines in some people.
Lack of sleep: Sleep deprivation or irregular sleep patterns can trigger migraines in some people.
Medications: Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives, vasodilators, and some blood pressure medications, have been known to trigger migraines in some people.
Physical factors: Strenuous exercise, poor posture, and muscle tension in the neck and shoulders can trigger migraines in some people.
It’s important to note that not all triggers affect everyone in the same way, and some people may not have any identifiable triggers. Keeping a headache diary can help identify triggers and patterns, which can be helpful in developing a treatment plan with a healthcare provider.

Where is migraine pain located?
There are several potential triggers for migraines, including changes in hormones, stress, certain foods and drinks, sensory stimuli such as bright lights or loud noises, changes in sleep patterns, and physical exertion. Identifying and avoiding triggers can be an important part of managing migraines, along with medication and other treatments.



saepe molestiae et ex blanditiis in consequuntur sunt aspernatur ipsam quaerat sunt voluptas ut ullam odio optio recusandae ea. eos accusantium nobis exercitationem qui magnam officiis tempora.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.